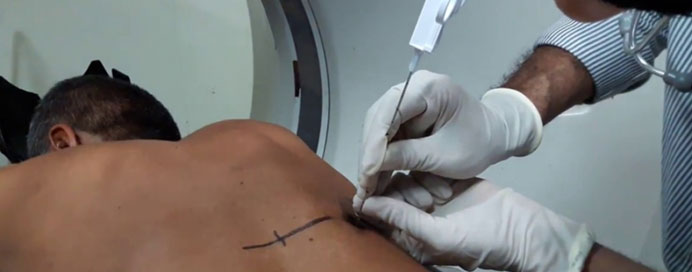
Lung Biopsy is a highly specialized diagnostic procedure used to obtain small tissue samples from the lungs to accurately identify infections, inflammatory conditions, or suspected lung cancer. Depending on the location and nature of the abnormality, the biopsy may be performed using advanced techniques such as CT-guided needle biopsy, bronchoscopic biopsy, transbronchial needle aspiration, or surgical biopsy in rare cases. These methods allow doctors to precisely target even small or deep lung lesions while minimizing discomfort and avoiding unnecessary surgery. Lung biopsy plays a crucial role in confirming the exact diagnosis, determining the type and stage of disease, and guiding the most appropriate treatment plan. With modern imaging and minimally invasive tools, the procedure is safe, efficient, and offers high diagnostic accuracy with quick recovery.