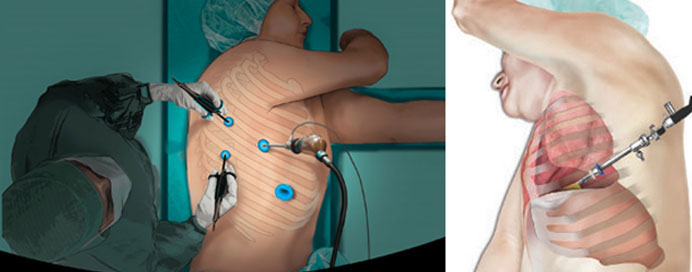
Medical Thoracoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that allows doctors to directly visualize the pleural space—the area between the lungs and chest wall—using a specialized endoscopic instrument. Performed under local anesthesia and conscious sedation, it helps diagnose and treat various pleural diseases without the need for major surgery. Through a small incision on the chest wall, the thoracoscope provides clear, magnified views of the pleura, enabling targeted biopsies, drainage of fluid, and therapeutic procedures such as pleurodesis. Medical Thoracoscopy is particularly valuable in evaluating unexplained pleural effusions, diagnosing tuberculosis or cancer, and managing recurrent fluid buildup around the lungs. Its safety, precision, and quick recovery make it an essential tool in modern respiratory and pleural care.