×
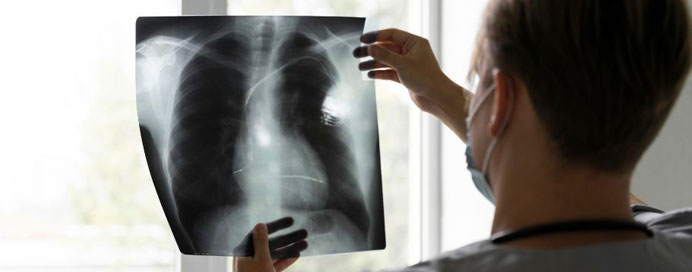
Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation of the air sacs in one or both lungs, leading to cough, fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, making it harder for oxygen to reach the bloodstream. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, and its severity ranges from mild illness to life-threatening infection, especially in young children, older adults, and people with weakened immunity. With timely diagnosis, proper antibiotics or antiviral treatment, and supportive care like oxygen therapy and hydration, most patients recover well. Early medical attention is crucial to prevent complications and ensure faster healing.
Important Links
Pulmonologist in Santacruz