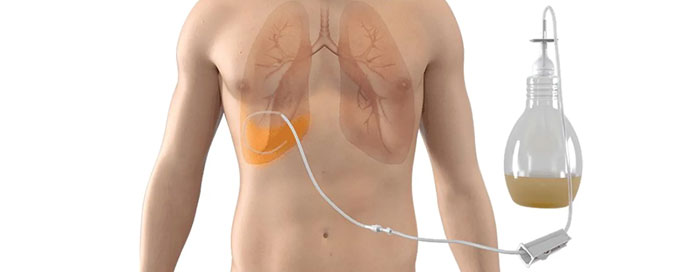
Tube Thoracostomy, commonly known as chest tube insertion, is a life-saving procedure used to drain air, fluid, blood, or pus from the pleural space to help the lungs fully expand again. Performed under local anesthesia and ultrasound or clinical guidance, a flexible plastic tube is carefully inserted between the ribs into the chest cavity. This allows continuous drainage, relieves breathlessness, stabilizes lung function, and treats conditions such as pneumothorax, hemothorax, empyema, and large pleural effusions. Tube Thoracostomy is one of the most effective and immediate interventions in respiratory and emergency care, offering rapid symptom relief and preventing severe complications.
- Effective Treatment for Lung Collapse (Pneumothorax): A chest tube removes trapped air from the pleural cavity, allowing the collapsed lung to re-expand quickly. This prevents respiratory distress, improves oxygen levels, and avoids the need for major surgery.
- Essential for Draining Fluid, Blood, or Infection: Tube Thoracostomy efficiently removes pleural effusions, hemothorax, and empyema. Continuous drainage helps reduce pressure on the lungs, alleviates pain, and supports faster recovery in patients with infections or trauma.
- Minimally Invasive but Highly Therapeutic: The procedure uses a small incision between the ribs and is performed under local anesthesia. Despite being minimally invasive, it provides maximum therapeutic benefit with quick, noticeable improvement in breathing.
- Enables Ongoing Monitoring and Medical Management: The chest tube allows doctors to monitor the amount, type, and rate of drainage, giving valuable diagnostic information. This helps guide further treatment such as antibiotics, pleurodesis, or surgery if required.
- Critical in Emergency and ICU Settings: Tube Thoracostomy is a cornerstone procedure in emergency medicine, trauma care, and ICUs. It rapidly stabilizes patients with life-threatening chest conditions, ensuring timely intervention and preventing complications like tension pneumothorax.
