×
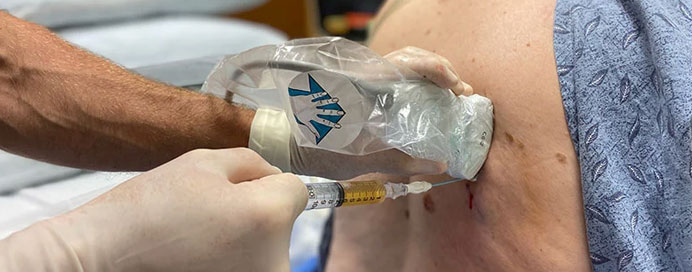
Thoracentesis is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to remove excess fluid from the pleural space—the thin area between the lungs and chest wall. Using ultrasound guidance, a fine needle or small catheter is carefully inserted through the chest to safely drain the accumulated fluid. This helps relieve symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest heaviness, and persistent cough while allowing doctors to analyze the fluid for infections, cancer, tuberculosis, or inflammatory diseases. Thoracentesis is quick, highly effective, and generally performed under local anesthesia, making it a safe and comfortable procedure with immediate improvement in breathing.